HemoSphere Vita monitor
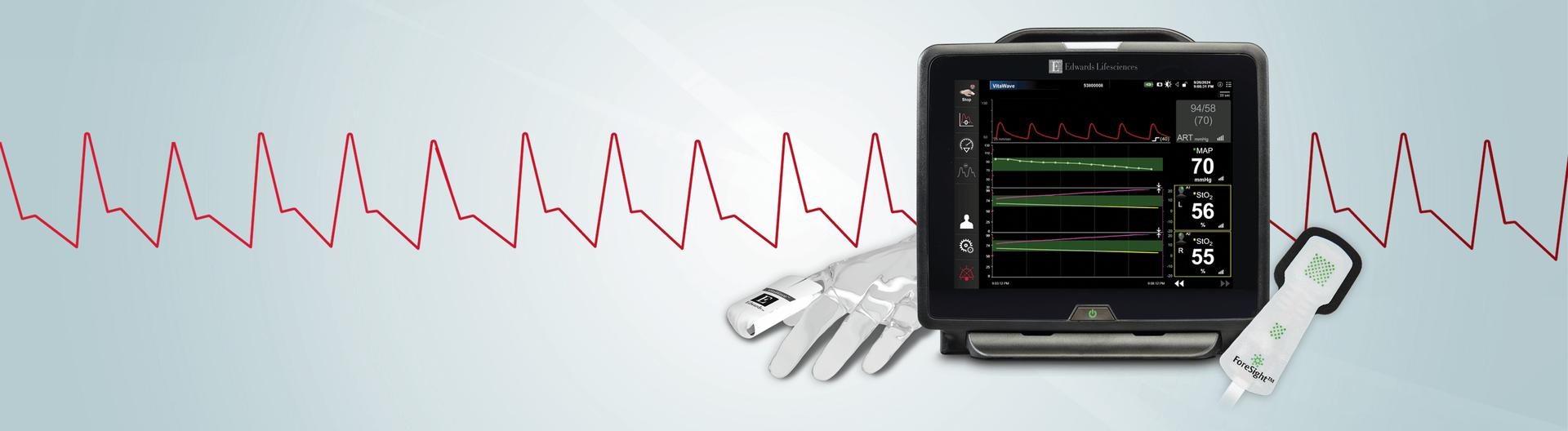
Edwards Lifesciences Critical Care product group is now part of BD (Becton, Dickinson and Company). Edwards is the manufacturer of the products.
To find the latest information, please visit this page on BD.com
Important safety information
Important safety information
CAUTION: Federal (United States) law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician.
See Instructions For Use (IFU) / Directions For Use (DFU) for full prescribing information, including indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions and adverse events.
