ICU Teams

Stay ahead of critical moments
In the ICU, you're at the patients bedside in their most vulnerable moments. For the rapidly changing and complex nature of the critically-ill patients, continuous information helps guide clinicians through the continuum of care. Advanced hemodynamic monitoring can aid you in the treatment of patients by providing actionable insights during the course of critical illness.
Shock management
Shock is common. 1/3 of ICU patients suffer some form of shock as Sakr, et all reported in 2006.1 Advanced hemodynamic measurements, like those provided by Acumen IQ sensor or Swan-Ganz catheter working with an advanced monitoring platform, can provide clinical insight into a patient’s cardiovascular function to guide decision- making.
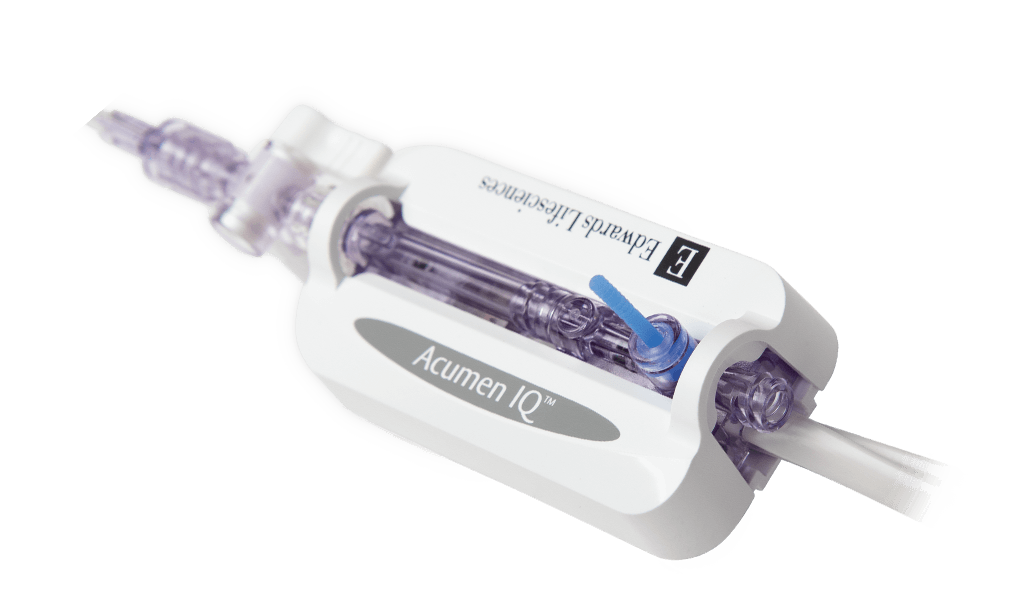

Acumen IQ sensor
Acumen IQ sensor unlocks Acumen HPI software and connects to any existing arterial line* to provide continuous blood pressure and advanced hemodynamic parameters. Acumen HPI software is the first-of-its-kind technology that detects hemodynamic instability and offers insight into potential targets for intervention.
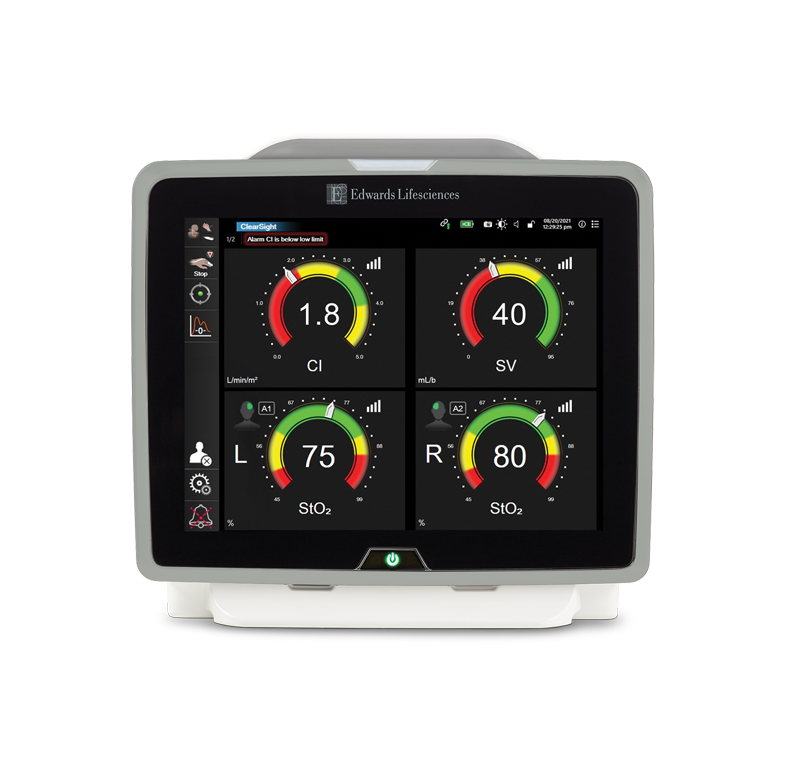
CO/CI | SV/SVI | SVV | PPV†| SVR/SVRI | Eadyn | dP/dt | SYS/DIA/MAP | HPI
*When using with Acumen HPI software, Acumen IQ sensor must be connected to a radial arterial line.
†PPV may not be available on earlier versions of HemoSphere monitor.
Perfusion management
Advanced hemodynamic monitoring provides access to continuous pressure and flow parameters, giving you valuable insight into the adequacy of perfusion. Dynamic parameters can help identify the most appropriate therapy, such as helping to decide between volume administration or the administration of vasopressors or inotropes.


Acumen IQ sensor
Acumen IQ sensor unlocks Acumen HPI software and connects to any existing arterial line* to provide continuous blood pressure and advanced hemodynamic parameters. Acumen HPI software is the first-of-its-kind technology that detects hemodynamic instability and offers insight into potential targets for intervention.
CO/CI | SV/SVI | SVV | PPV†| SVR/SVRI | Eadyn | dP/dt | SYS/DIA/MAP | HPI
*When using with Acumen HPI software, Acumen IQ sensor must be connected to a radial arterial line.
†PPV may not be available on earlier versions of HemoSphere monitor.
COVID-19 support
Patients who require hospitalization for COVID-19 are at an increased risk of developing conditions such as sepsis, acute kidney injury (AKI), and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).2 Clinicians around the world are in constant discussions on how best to care for, treat, and manage patients with COVID-19 and the resulting sepsis, septic shock, and/or acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Learn about the monitoring solutions that help clinicians in managing ideal oxygenation and maintaining appropriate fluid balance to minimize severe life-threatening complications.

Tissue oximetry
Tissue oxygen (StO2) desaturation events are not uncommon in the cardiac and surgical ICU's. For the most critically ill patients requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), tissue oximetry monitoring may help allow early identification of cerebral desaturations and limb ischemia.3,4
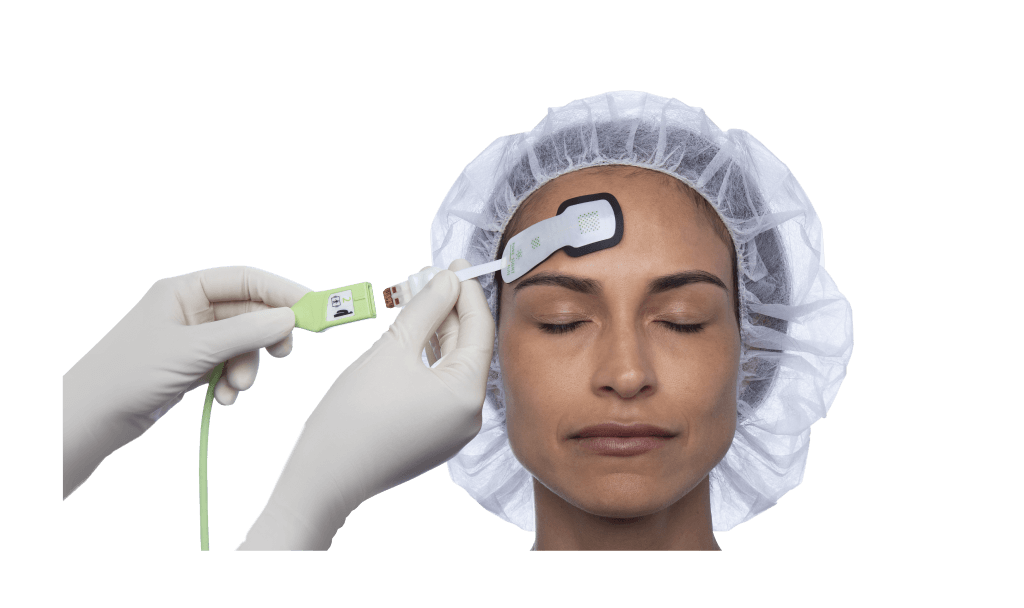
ForeSight tissue oximetry sensor
ForeSight sensor delivers absolute StO2 values that – when used in combination with the full hemodynamic insights delivered by HemoSphere advanced monitoring platform – enable you to confidently recognize and address cerebral desaturations and limb ischemia.
Pressure monitoring and blood conservation
You can make a difference in your patients’ outcomes by incorporating evidence-based closed blood sampling (CBS) procedures into your hospital’s patient blood management program. CBS is demonstrated to more effectively conserve blood, improve patient outcomes and reduce costs when compared with conventional blood sampling procedures.5-8
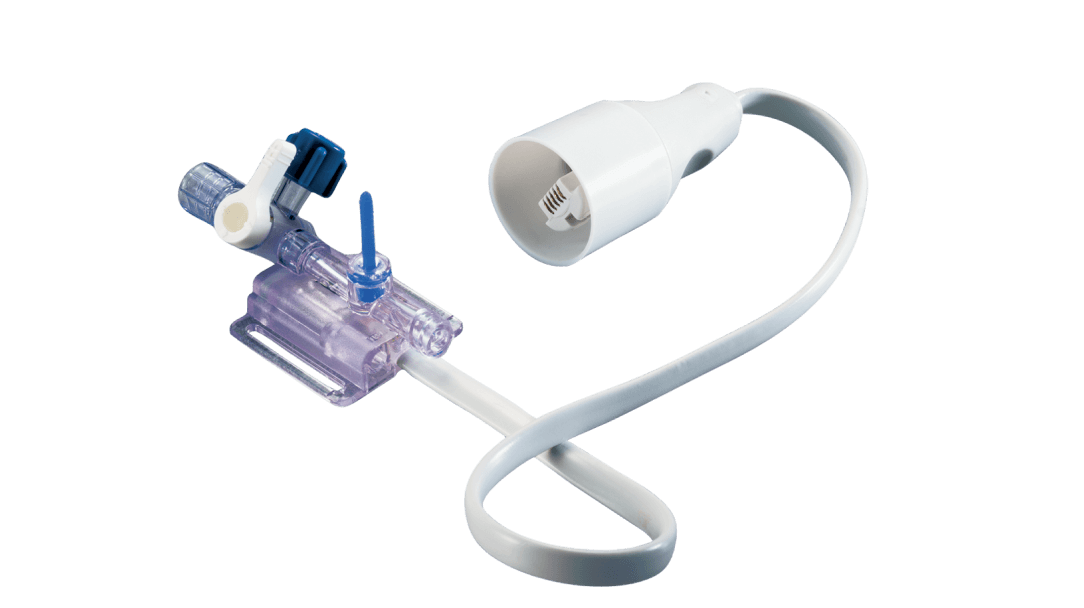


TruWave pressure transducers
TruWave disposable pressure transducers may be used independently or combined with VAMP closed blood sampling systems for a single safe, reliable and accurate monitoring solution.
Edwards clinical education
With a long-term commitment to improving the quality of care for surgical and critical care patients through education, Edwards clinical education meets you no matter where you are in the learning process—with a continuum of resources and tools that continuously support you as you solve the clinical challenges facing you today, and in the future.

References
- Sakr Y, Reinhart K, Vincent JL, et al. Does dopamine administration in shock influence outcome? Results of the Sepsis Occurrence in Acutely Ill Patients (SOAP) Study. Crit Care Med 2006. 589 – 597.
- World Health Organization Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection (SARI) when COVID-19 disease is suspected: Interim guidance V 1.2
- Patton-Rivera, et al. Using near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy (NIRS) to assess distal-limb perfusion on venoarterial (V-A) extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) patients with femoral cannulation. Perfusion 2018. 1-6.
- Greenberg, et al. Cerebral desaturation events in the intensive care unit following cardiac surgery. Journal of Critical Care 2013. 270-276.
- Peruzzi, W.T., et al., A clinical evaluation of a blood conservation device in medical intensive care unit patients. Critical care medicine, 1993. 21 (4): p. 501-6
- Oto, J., et al., Comparison of bacterial contamination of blood conservation system and stopcock system arterial sampling lines used in critically ill patients. American Journal of Infection Control, 2012. 40(6): p.530-4
- O'Hare, D. and R.J. Chilvers, Arterial blood sampling practices in intensive care units in England and Wales. Anaesthesia, 2001. 56(6): p. 568-71
- Tang, M., et al,. Closed Blood Conservation Device for Reducing Catheter-Related Infections in Children After Cardiac Surgery. Critical Care Nurse, 2014. 34(5); p.53-61
Important safety information
CAUTION: Federal (United States) law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician.
See Instructions For Use (IFU) / Directions For Use (DFU) for full prescribing information, including indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions and adverse events.