Low incidence of hypotension
41% of patients avoided hypotension when monitored with Acumen HPI software, compared to 12% of patients in another large multicenter study where Acumen HPI software was not used.*1,2
Unlock intelligent decision support
Edwards Lifesciences Critical Care product group is now part of BD (Becton, Dickinson and Company). Edwards is the manufacturer of the products.
To find the latest information, please visit this page on BD.com
41% of patients avoided hypotension when monitored with Acumen HPI software, compared to 12% of patients in another large multicenter study where Acumen HPI software was not used.*1,2
Patients in this study experienced approximately 2 minutes of hypotension, or 1% of surgery time, compared with 28 minutes in another large multicenter study where Acumen HPI software was not used.* 1,2
Patients monitored with Acumen HPI software experienced a very low TWA MAP <65 mmHg, at 0.03. The TWA MAP <60 mmHg was 0.*1
*Multicenter, prospective, observational study of over 700 noncardiac surgery patients across 5 countries monitored with Acumen IQ arterial line sensor. Hypotension defined as >1 min below MAP 65 mmHg.
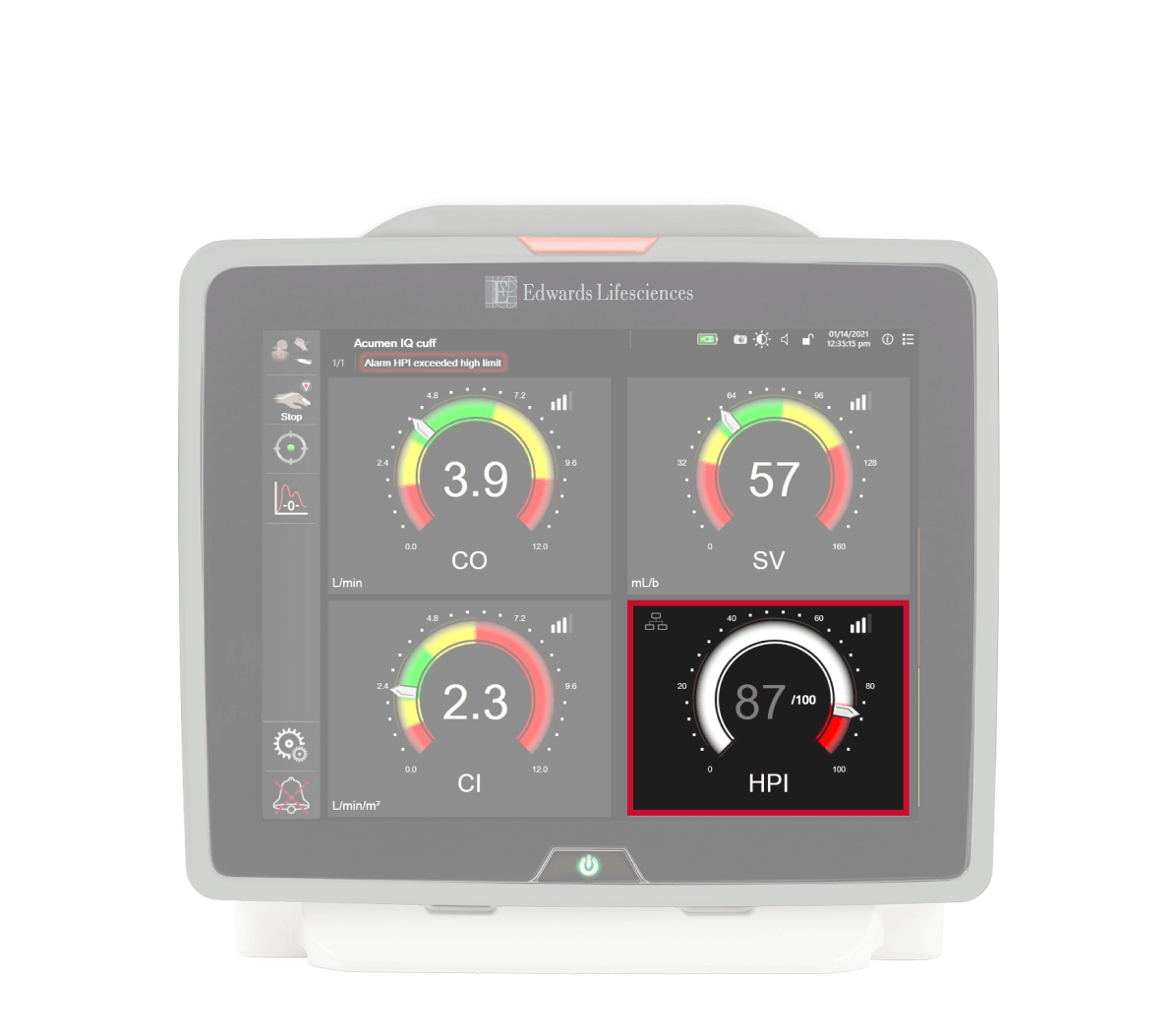
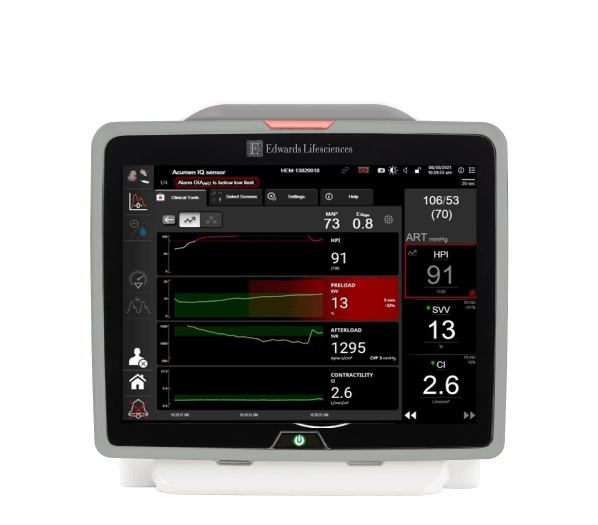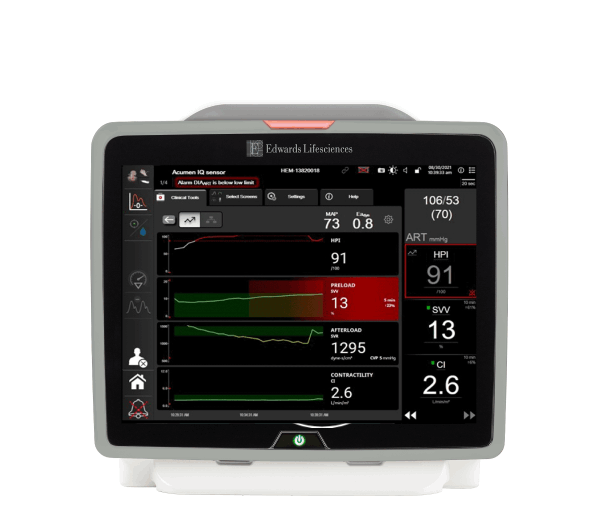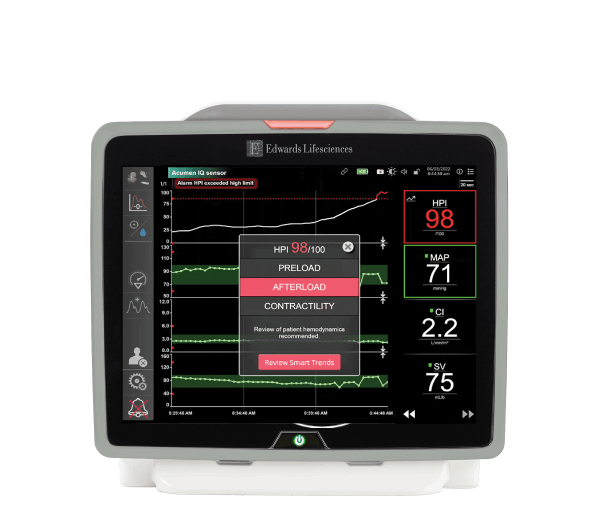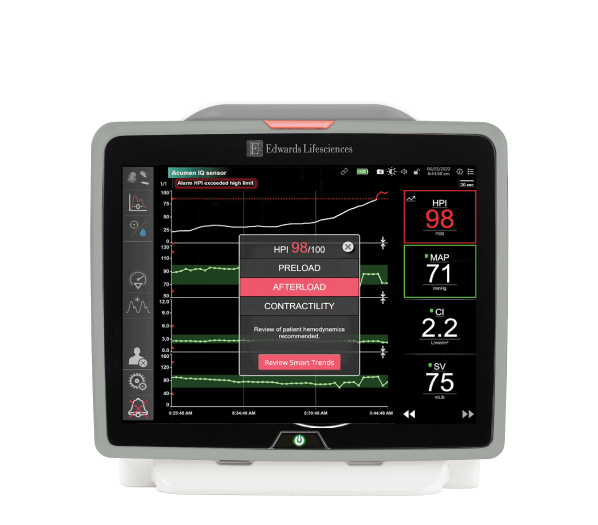
The HPI parameter displays as a value ranging from 0 to 100, with higher values indicating higher likelihood of a hypotensive event.**
The HPI parameter value is updated every 20 seconds, providing continuous predictive insights into developing hypotension.

The smart alerts popup alerts you when your patient may be trending toward a hypotensive event.**
Smart alerts and trends provide you with a focused view of the potential targets for intervention such as preload, afterload and contractility - so you can prevent or treat hypotension upon review of the patient's complete hemodynamic state.
The relationship view screen provides you insights into the cause of hypotension, and hemodynamic parameters are arranged visually by preload, afterload and contractility.
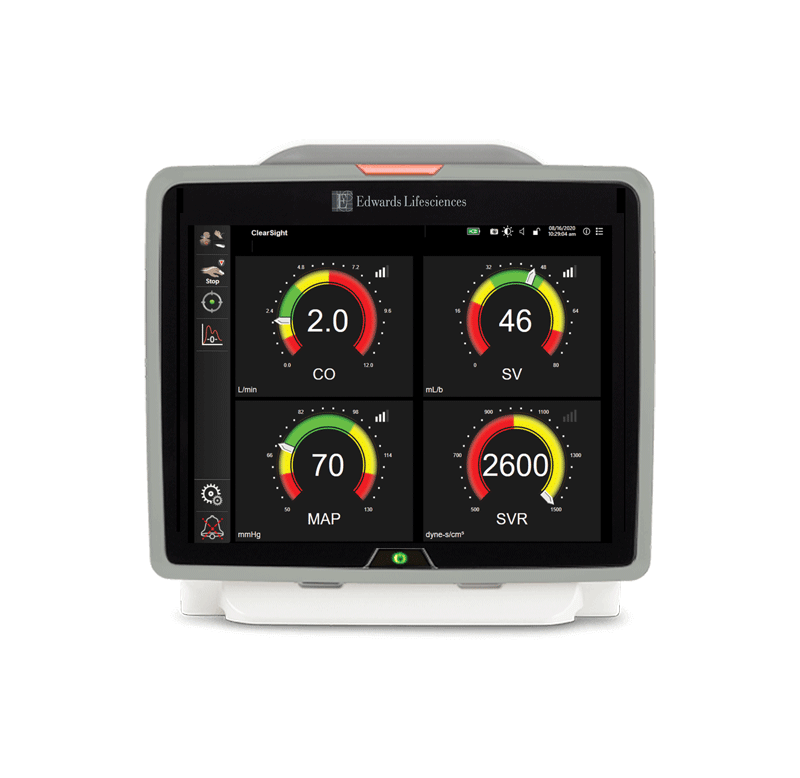
It provides hemodynamic information associated with hypotension, including several key parameters such as MAP, CO, SVR, PR, and SV, as well as HPI, dP/dt, and Eadyn

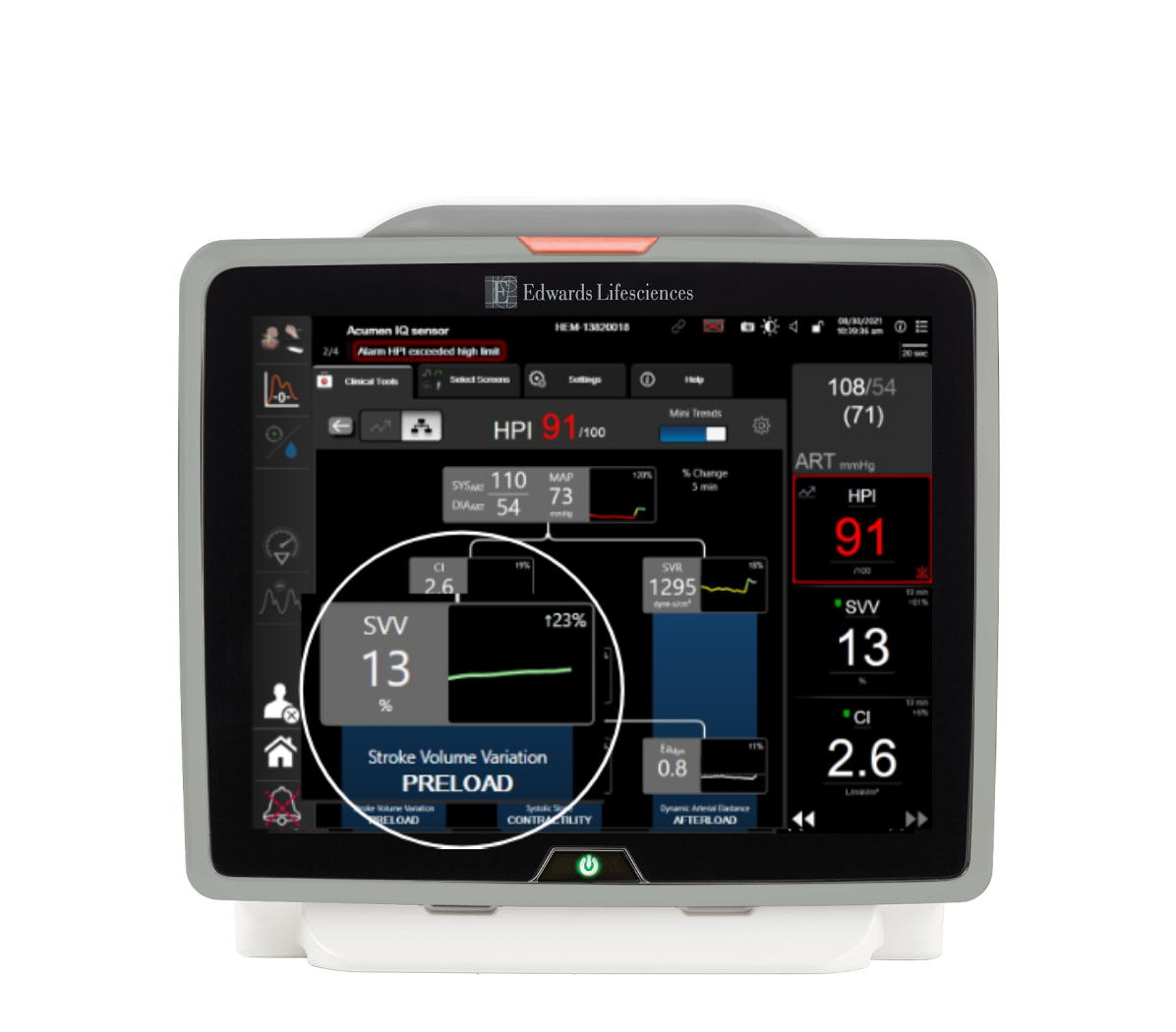
Stroke volume variation (SVV) or pulse pressure variation (PPV)
The percent difference between minimum and maximum stroke volume (SV) or pulse pressure (PP) during a respiratory cycle.

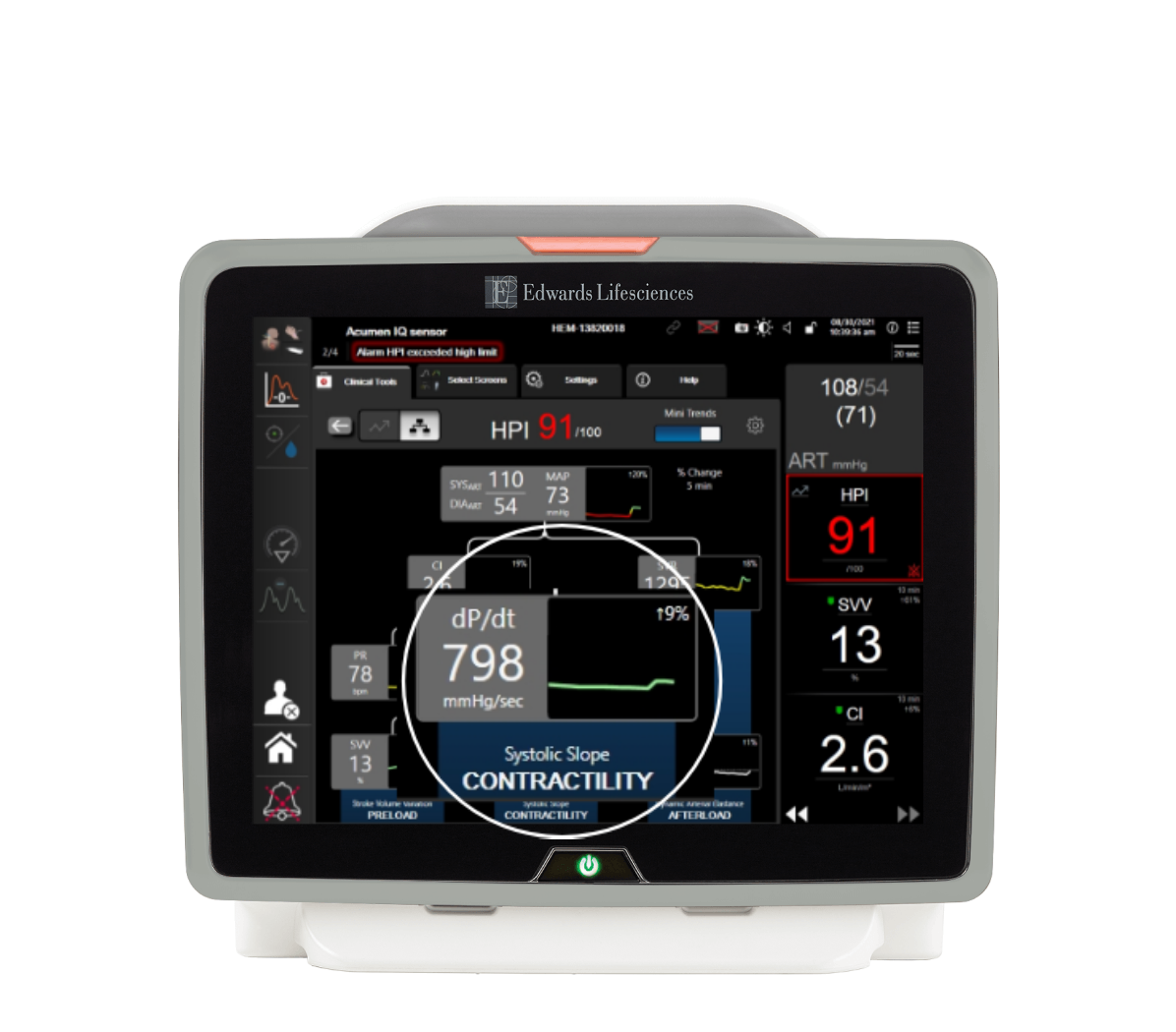
Systolic slope (dP/dt)
Maximum upslope of the arterial pressure waveform from a peripheral artery.

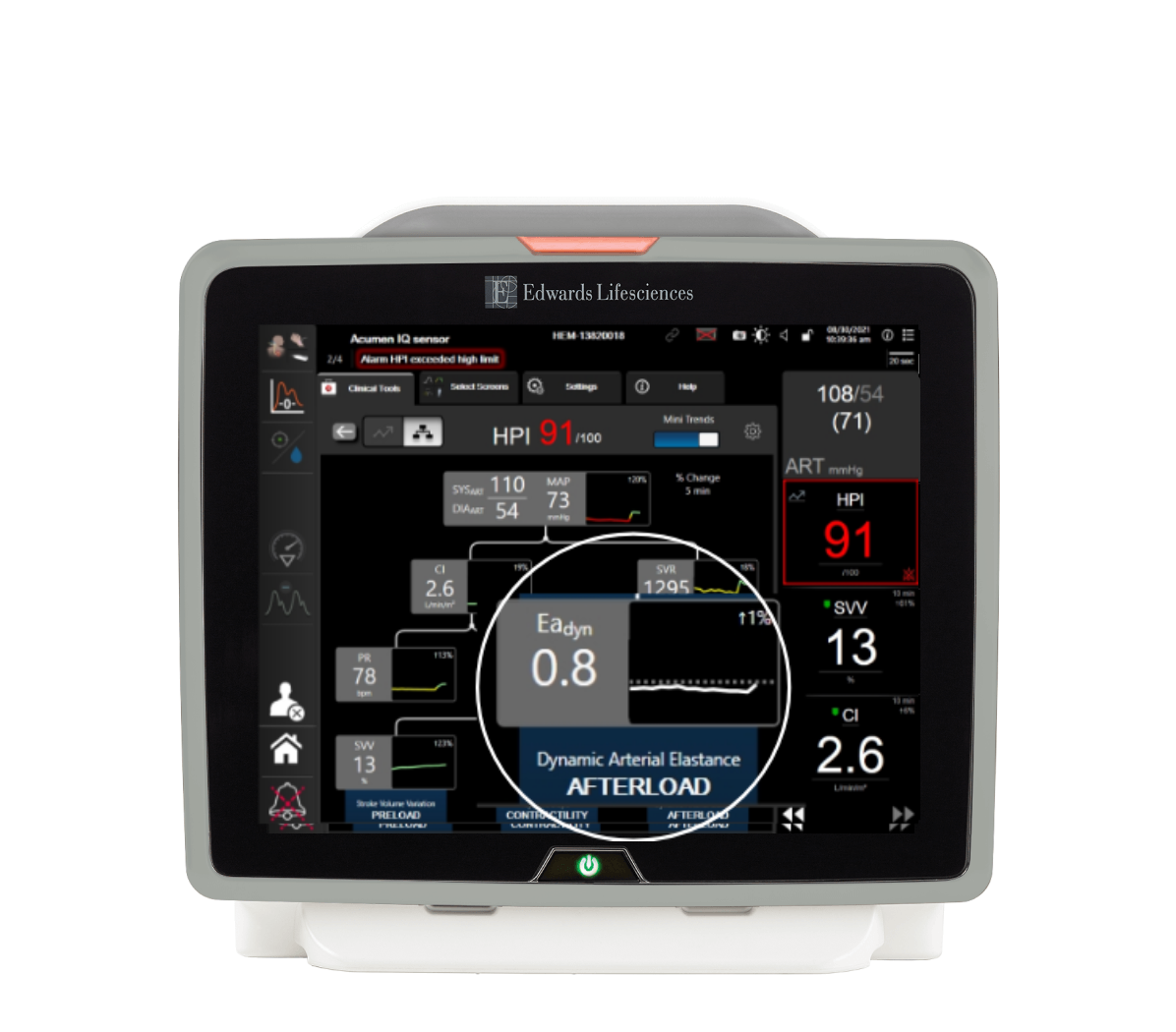
Dynamic arterial elastance (Eadyn)
The ratio of pulse pressure variation to stroke volume variation.
System vascular resistance (SVR)
Derived measure of impedance of blood flow from the left ventricle







The HPI parameter displays as a value ranging from 0 to 100, with higher values indicating higher likelihood of a hypotensive event.**
The HPI parameter value is updated every 20 seconds, providing continuous predictive insights into developing hypotension.
The smart alerts popup alerts you when your patient may be trending toward a hypotensive event.**
Smart alerts and trends provide you with a focused view of the potential targets for intervention such as preload, afterload and contractility - so you can prevent or treat hypotension upon review of the patient's complete hemodynamic state.
The relationship view screen provides you insights into the cause of hypotension, and hemodynamic parameters are arranged visually by preload, afterload and contractility.
It provides hemodynamic information associated with hypotension, including several key parameters such as MAP, CO, SVR, PR, and SV, as well as HPI, dP/dt, and Eadyn
Stroke volume variation (SVV) or pulse pressure variation (PPV)
The percent difference between minimum and maximum stroke volume (SV) or pulse pressure (PP) during a respiratory cycle.
Systolic slope (dP/dt)
Maximum upslope of the arterial pressure waveform from a peripheral artery.
Dynamic arterial elastance (Eadyn)
The ratio of pulse pressure variation to stroke volume variation.
System vascular resistance (SVR)
Derived measure of impedance of blood flow from the left ventricle
**A hypotensive event is defined as MAP <65 mmHg for a duration of at least one minute.
Review clinical evidence and validation studies for Acumen HPI software
Though intraoperative hypotension (IOH) is common in surgical patients, numerous studies indicate that it is strongly associated with risk of myocardial injury (MI), acute kidney injury (AKI), and mortality.3,4,7
Acumen HPI software is effective in detecting hemodynamic instability and substantially reducing the duration of IOH during noncardiac surgery.8*
*Compared to a retrospective historical control group, in noncardiac surgical patients requiring arterial line monitoring1
88% of patients continuously monitored with an arterial line still experienced hypotension, defined as MAP <65 mmHg for 1 minute.2
Prolonged exposures below MAP thresholds of 65 mmHg are associated with increased risk of mortality, myocardial injury and AKI after noncardiac surgery.3,9
Studies show: Use of Acumen HPI software significantly reduced hypotension.8
*Prospective, single-arm multicenter study in noncardiac surgical patients requiring arterial line monitoring compared to a historical control
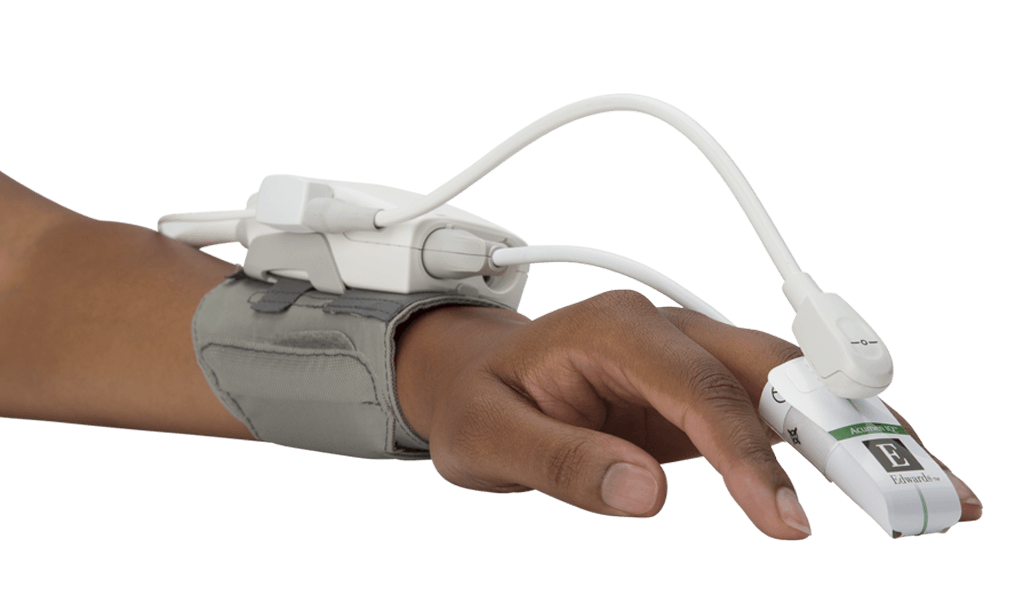
Acumen IQ cuff unlocks Acumen HPI software* and provides continuous blood pressure and advanced hemodynamic parameters from a noninvasive finger cuff.
* Acumen HPI parameter is indicated for surgical patients only when using an Acumen IQ cuff
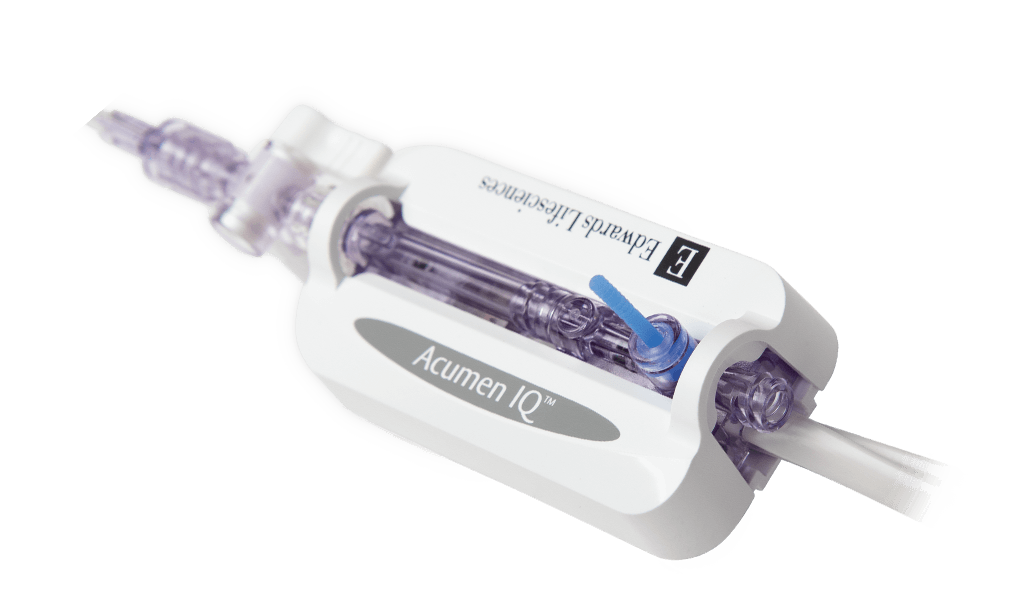
Acumen IQ sensor unlocks Acumen HPI and Acumen Assisted Fluid Management (AFM) software. The sensor connects to any existing radial arterial line and offers you patients’ hemodynamic status.
With a long-term commitment to improving the quality of care for surgical and critical care patients through education, Edwards clinical education meets you no matter where you are in the learning process — with a continuum of resources and tools that continuously support you as you solve the clinical challenges facing you today, and in the future.
CAUTION: Federal (United States) law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician.
See Instructions For Use (IFU) / Directions For Use (DFU) for full prescribing information, including indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions and adverse events.
We are committed to providing your institution, clinicians and staff with the highest levels of customer service and support to ensure seamless product implementation and ongoing use, including:
24/7 Technical support
For product information and orders