
COMMENCE mitral clinical trial1
Clinically stable hemodynamics and one incident of structural valve deterioration (SVD) through 5 years in 82 patients.
Clinical evidence

Backed by a strong and growing body of clinical evidence supported by RESILIA* tissue’s ongoing study of durability and hemodynamic performance1–3

Clinically stable hemodynamics and one incident of structural valve deterioration (SVD) through 5 years in 82 patients.
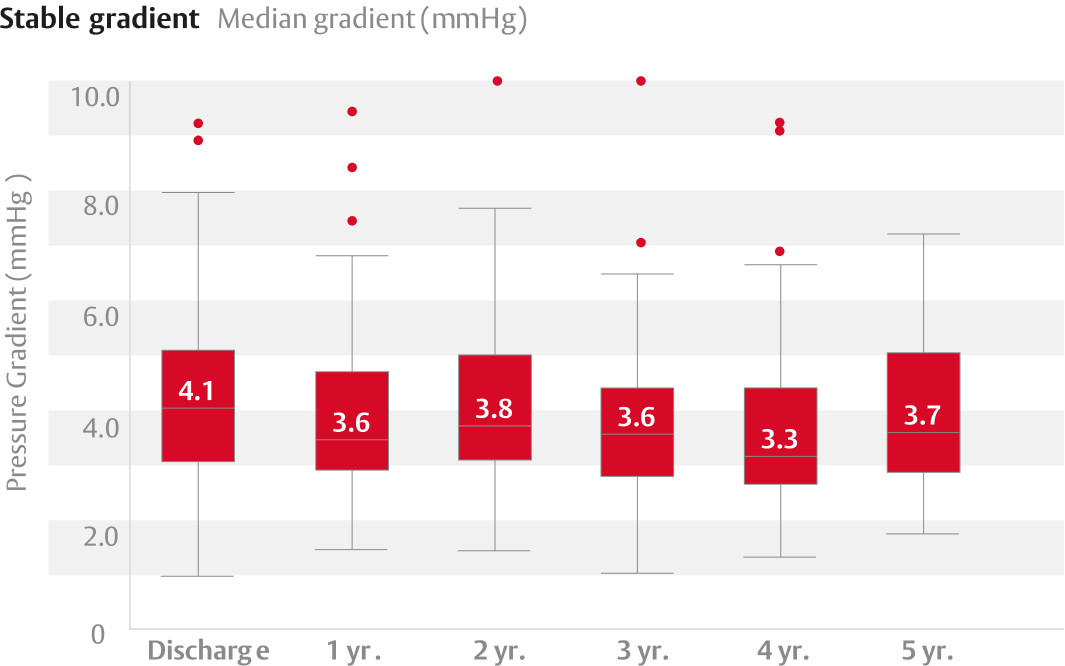

Clinically stable hemodynamics and two incidents of SVD through 7 years.
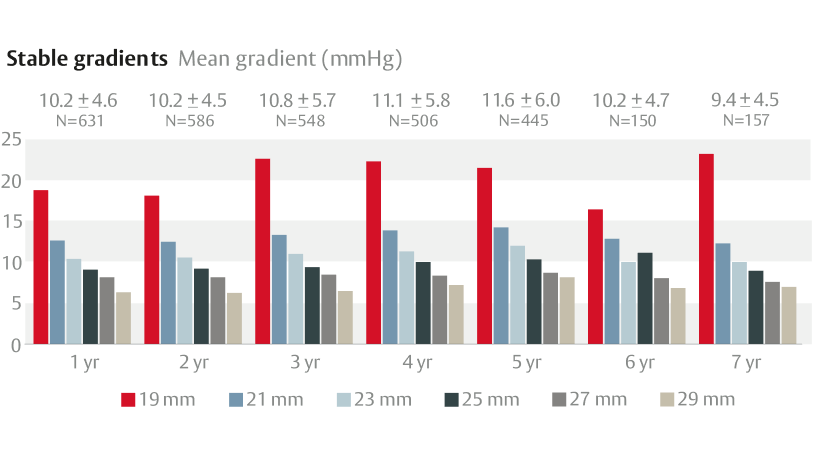

Clinically stable hemodynamics and zero SVD through 5 years in 133 patients.

Post-operative outcomes varied among the three mitral bioprostheses:†
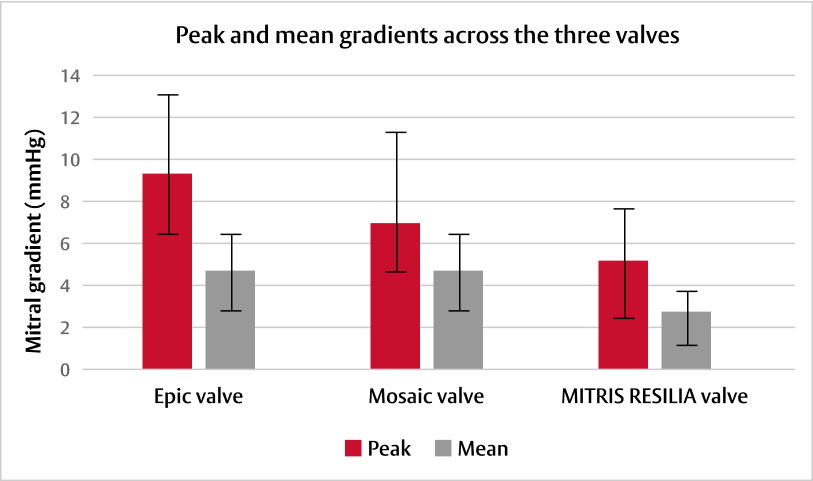
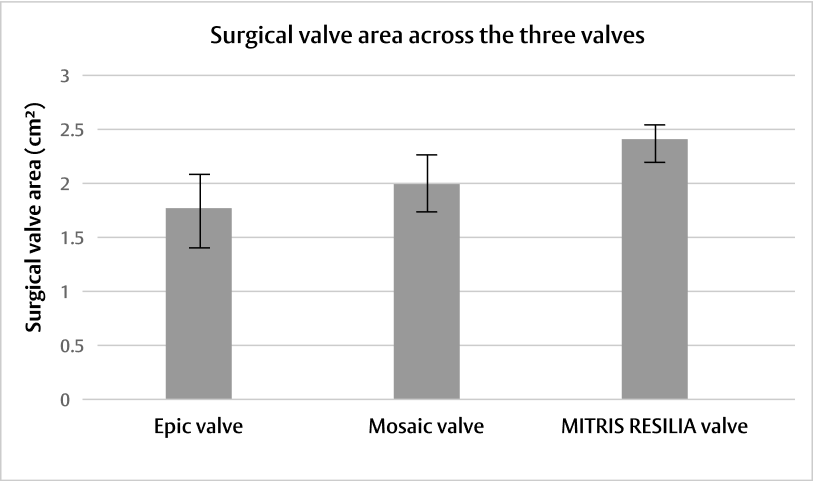
Adapted from Wang DD, et al. J Card Surg. 2021.4

Adapted from Wang DD, et al. J Card Surg. 2021.4
†Preclinical early feasibility experimental study evaluating three mitral bioprostheses (27 mm Epic valve, Abbott [n=4], 27 mm Mosaic valve, Medtronic [n=4], and 25 mm MITRIS RESILIA valve, Edwards Lifesciences [n=4]) under controlled, stable, haemodynamic and surgical conditions. Yorkshire pigs underwent implantation via thoracotomy on cardiopulmonary bypass. Epicardial echocardiographic studies were performed to assess haemodynamic function and define paravalvular leak, followed by contrast computerised tomography.
*No clinical data are available that evaluate the long-term impact of RESILIA tissue in patients. Additional clinical data for up to 10 years of follow-up are being collected to monitor the long-term safety and performance of RESILIA tissue.
For a listing of indications, contraindications, precautions, warnings, and potential adverse events, please refer to the Instructions for Use (consult eifu.edwards.com where applicable).