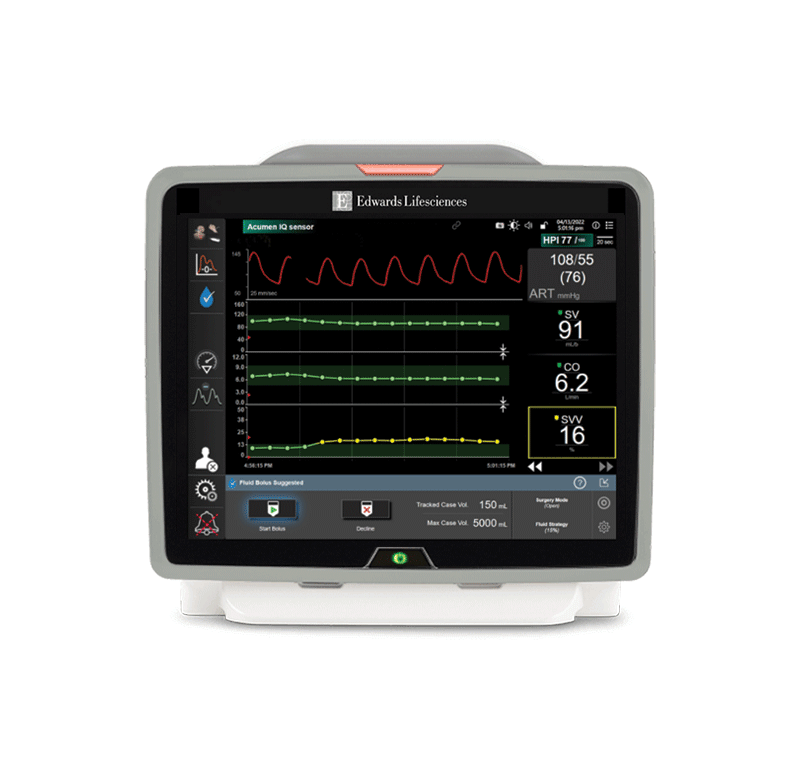
OR
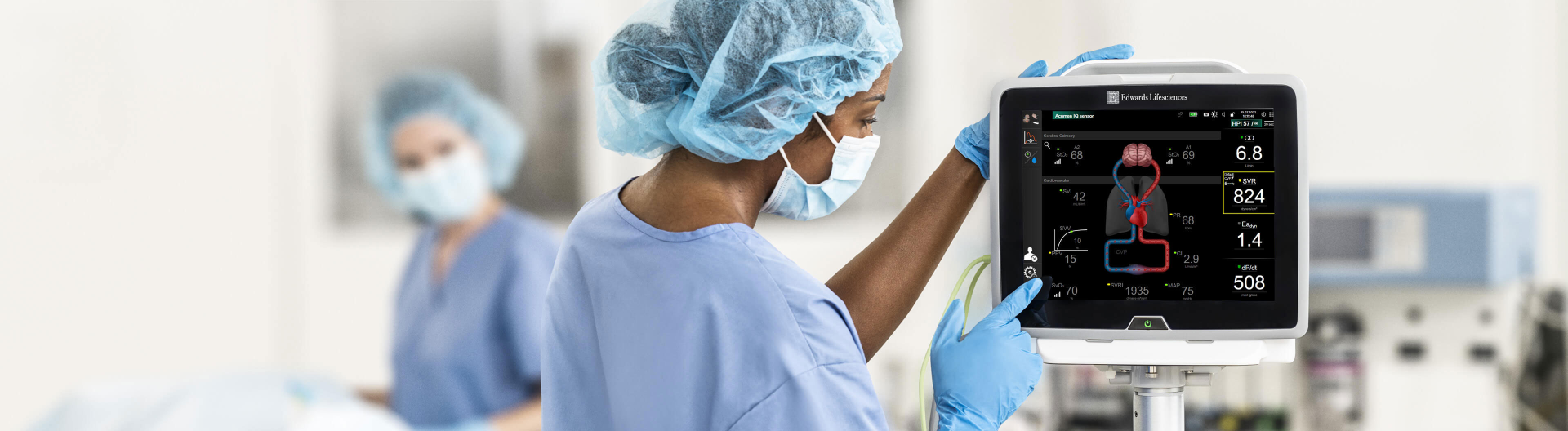
Stay ahead of critical moments
In the OR, every second counts. And as an anesthesiologist or anesthesia assistant, patient safety is your number-one priority. Today you are faced with an increasingly complex patient population. HemoSphere advanced monitoring platform provides a comprehensive view of tissue oximetry and hemodynamics, giving you confidence in knowing continuous oxygen saturation and perfusion.
For more than 50 years, Edwards Lifesciences has been helping you make proactive clinical decisions and advance the care of surgical and acutely ill patients across the continuum of care.
Hypotension management
Intraoperative hypotension matters. Recent studies show associations between intraoperative hypotension and increased risk of acute kidney injury (AKI) and myocardial injury1-3 — the leading cause of post-operative mortality within 30 days after surgery.1 Prolonged exposures below mean arterial pressure (MAP) thresholds of 65 mmHg are associated with an increased risk of myocardial injury and AKI after noncardiac surgery.1
Related products
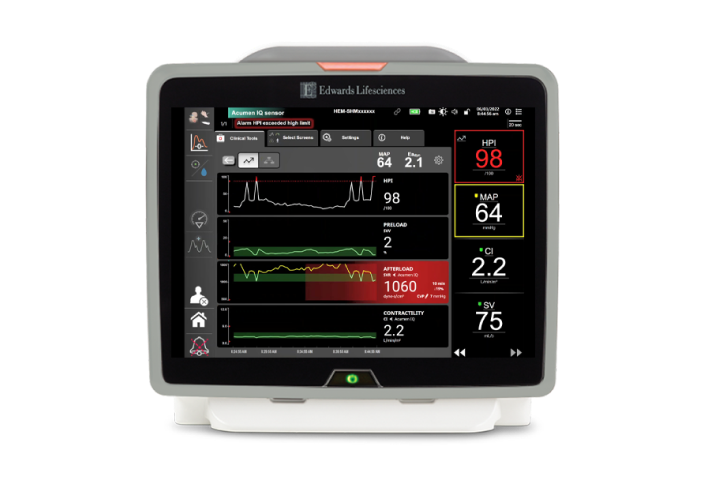

Acumen Hypotension Prediction Index (HPI) software
Developed in partnership with clinicians, our first-of-its-kind predictive decision support software detects the likelihood of a patient trending towards a hypotensive event* before the event occurs, and provides you with insights to understand the root cause and inform a potential course of action for your patient.
Studies have shown that Acumen HPI software:
- Achieves statistically significant reduction of hypotension when combined with a treatment protocol in noncardiac surgery vs. standard of care4,5
- Demonstrates superior predictive abilities for hypotension than common hemodynamic parameters such as cardiac output (CO), stroke volume (SV), and changes in mean arterial pressure (MAP)6
- Has proven and reliable accuracy7
Perfusion optimization
Advanced hemodynamic monitoring provides access to continuous pressure and flow parameters, giving you valuable insight into the adequacy of perfusion. Dynamic parameters can help identify the most appropriate therapy, such as helping to decide between volume administration or the administration of vasopressors or inotropes.
Related products

ClearSight system
The ClearSight finger cuff provides advanced hemodynamic parameters and continuous noninvasive blood pressure (BP) monitoring. The noninvasive ClearSight system allows continuous assessment of your patients' physiological needs, enabling you to evaluate hemodynamic instability and guide appropriate treatment.
Parameters
CO/CI | SV/SVI | SVR/SVRI | MAP
Tissue oximetry management
Gain access to oxygenation insights you can act on to ensure confident decisions with reliable, real-time monitoring of surgical patients that supports detecting and managing hypoxic events as they occur.
Related products

ForeSight Elite tissue oximetry system
Continuously monitors tissue oximetry, noninvasively, giving you a comprehensive view of tissue oxygenation and advanced hemodynamics on one monitor so you can ensure your patient is adequately perfused.
Parameters
StO2
References
- Salmasi, V., Maheshwari, K., Yang, G., Mascha, E.J., Singh, A., Sessler, D.I., & Kurz, A. (2017). Relationship between intraoperative hypotension, defined by either reduction from baseline or absolute thresholds, and acute kidney injury and myocardial injury. Anesthesiology, 126(1), 47-65.
- Sun, L.Y., Wijeysundera, D.N., Tait, G.A., & Beattie, W.S. (2015). Association of Intraoperative Hypotension with Acute Kidney Injury after Elective Noncardiac Surgery. Anesthesiology, 123(3), 515-523.
- Walsh, M., Devereaux, P.J., Garg, A.X., Kurz, A., Turan, A., Rodseth, R.N., Cywinski, J., Thabane, L., & Sessler, D.I. (2013). Relationship between Intraoperative Mean Arterial Pressure and Clinical Outcomes after Noncardiac Surgery. Anesthesiology, 119(3), 507-515.
- Wijnberge, M., Geerts, B., Hol, L., Lemmers, N., Mulder, M., Berge, P., Schenk, J., Terwindt, L., Hollman, M., Vlaar, A., Veelo, D. (2020) Effect of a Machine Learning-Derived Early Warning System for Intraoperative Hypotension vs Standard Care on Depth and Duration of Intraoperative Hypotension During Elective Noncardiac Surgery: The HYPE Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Online, February 17, 2020. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.0592 https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/article-abstract/2761469
- Schneck, E., Schulte, D., Habig, L., Ruhrmann, S., Edinger, F., Markmann, M., Habicher, M., Rickert, M., Koch, C., Sander, M. (2019) Hypotension Prediction Index based protocolized haemodynamic management reduces the incidence and duration of intraoperative hypotension in primary total hip arthroplasty: a single centre feasibility randomized blinded prospective interventional trial. Journal of Clinical Monitoring and Computing online, November 29, 2019. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10877-019-00433-6
- Davies SJ, Vistisen ST, Jian Z, et al. Ability of an arterial waveform analysis-derived hypotension prediction index to predict future hypotensive events in surgical patients. Anesth Analg 2019;doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000004121. https://journals.lww.com/anesthesia-analgesia/Citation/2020/02000/Ability_of_an_Arterial_Waveform_Analysis_Derived.16.aspx
- Hatib, F., Zhongping, J., Buddi, S., Lee, C., Settels, J., Sibert, K., Rinehart, J., Cannesson, M. (2018). Machine-learning Algorithm to Predict Hypotension Based on High-fidelity Arterial Pressure Waveform Analysis. Anesthesiology 129, 663-74. https://anesthesiology.pubs.asahq.org/article.aspx?articleid=2685008
Medical device for professional use
For a listing of indications, contraindications, precautions, warnings, and potential adverse events, please refer to the Instructions for Use (consult eifu.edwards.com where applicable).