Acumen Analytics software

Acumen Analytics software offers you retrospective data analysis and haemodynamic insights into patient perfusion, all on your personal computer.
Acumen Analytics software allows you to retrospectively view and analyse monitored haemodynamic parameters from the HemoSphere advanced monitoring platform when used with Acumen IQ cuff, Acumen IQ sensor, ClearSight finger cuff, FloTrac sensor, or ForeSight sensor.
When using any of the blood pressure monitoring cuffs and sensors (Acumen IQ cuff, Acumen IQ sensor, ClearSight finger cuff, or FloTrac sensor), Acumen Analytics software allows you to highlight key events including:

Hypotension duration
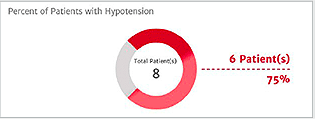
Hypotension prevalence
How Acumen Analytics software works
Analyse
Acumen Analytics software analyses retrospective haemodynamic parameter data from the HemoSphere advanced monitoring platform when used with an Acumen IQ cuff, Acumen IQ sensor, ClearSight finger cuff, FloTrac sensor or ForeSight sensor.
Transfer
Monitoring sessions can be downloaded from the HemoSphere advanced monitoring platform onto the Acumen Analytics software on your desktop or laptop computer. The report includes demographics data that you can organise and analyse. Patient identifiers are omitted from the data.

Review
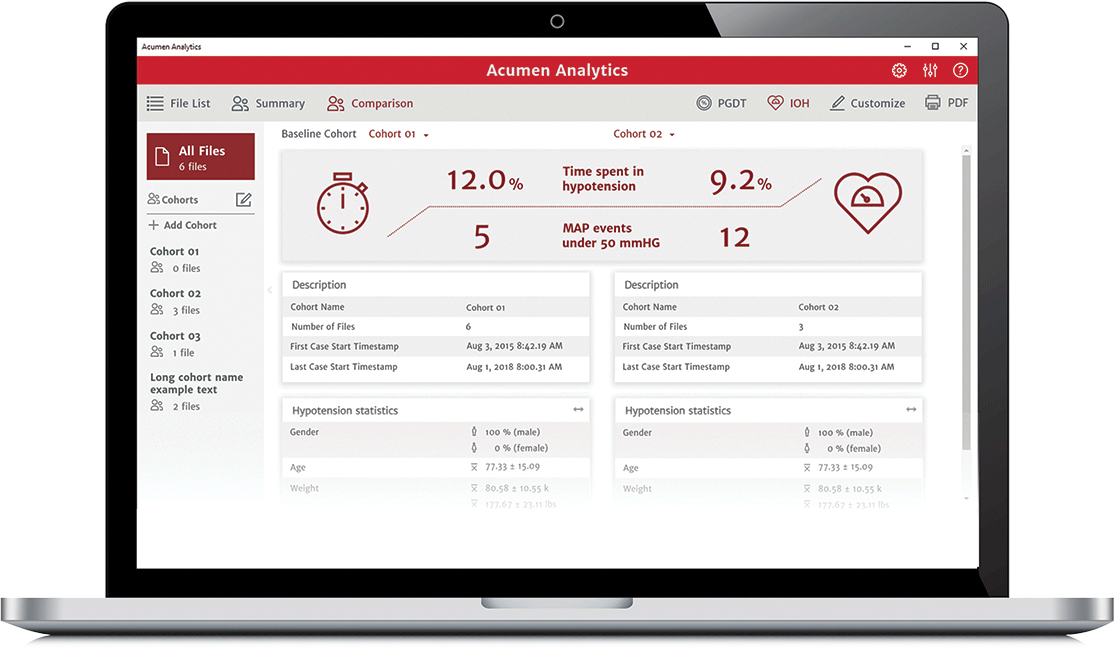
The Acumen Analytics software primary screen allows you to retrospectively analyse data within and between cohorts or for individual patients.
Key features of Acumen Analytics software
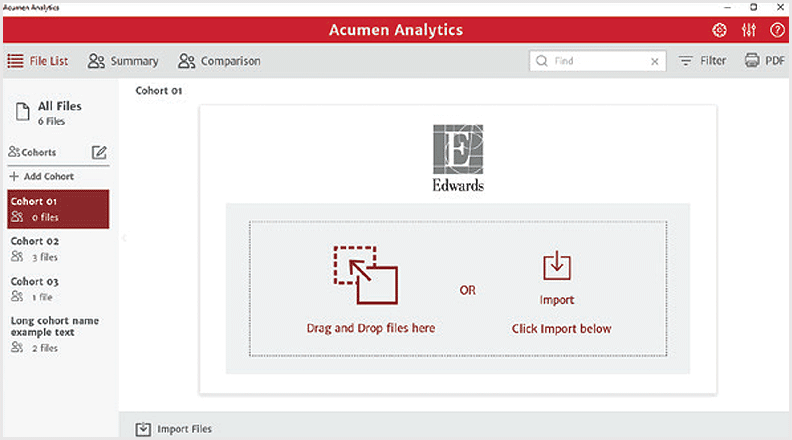
Customisable viewing pane
With a streamlined and customisable tile layout, the main viewing page organises a list of all cases, cohort summaries, and cohort comparison for convenient overviews.
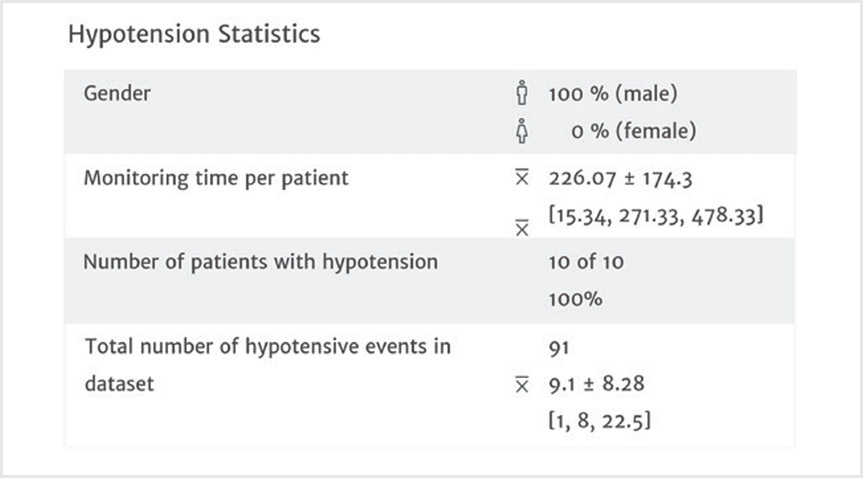
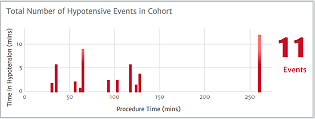
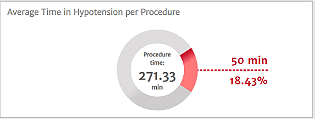
Hypotension statistics
This case summary list provides statistics on key hypotensive calculations such as average number of hypotensive events*, duration of each event, number of patients in a cohort that experienced hypotension.
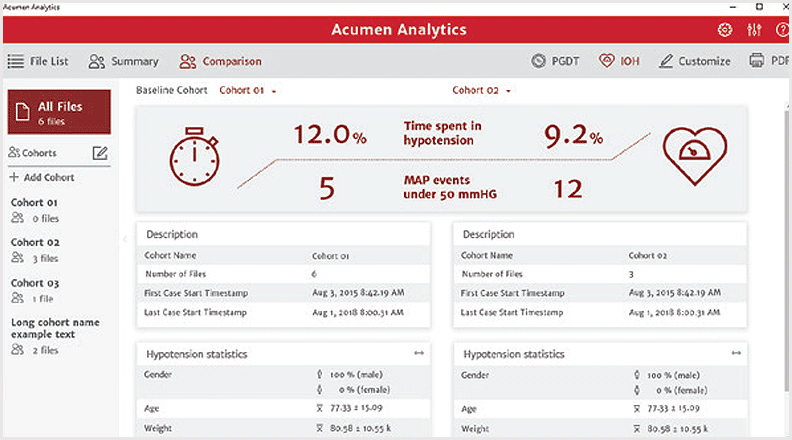
Cohort comparison
The cohort comparison screen allows you to retrospectively compare data from two cohorts. Hypotension data includes duration of hypotension and mean arterial pressure (MAP) events. The customisable cohort summary screen displays a summary of the data collected for the chosen patient or patient group.
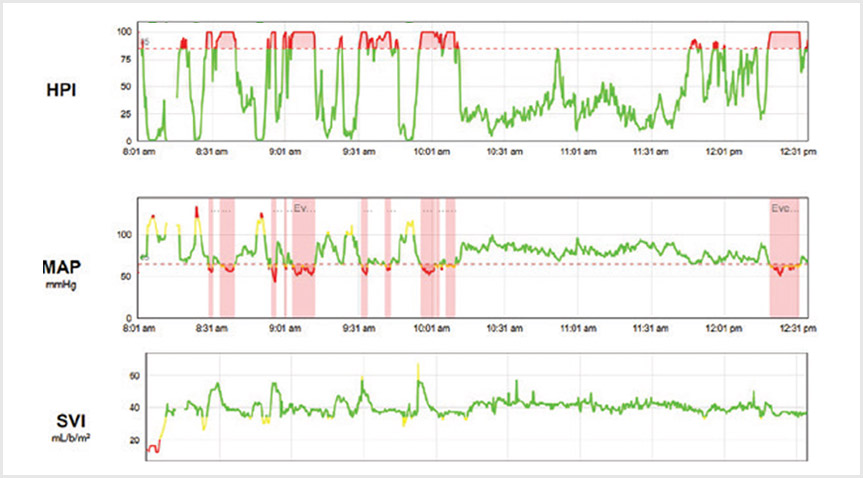
Trend parameters
At the core of Acumen Analytics software is advanced haemodynamic parameter data. You can review recorded data on a number of valuable pressure and flow parameters as well as tissue oxygen saturation from the HemoSphere monitoring platform. See chart below for available parameters.
| Parameter | Description |
| Hypotension Prediction Index (HPI) | Indicates the likelihood of a patient trending towards a hypotensive event* |
| Dynamic arterial elastance (Eadyn) | Ratio of pulse pressure variation (PPV) to stroke volume variation (SVV). It's an estimate of arterial elastance. |
| Systolic slope (dP/dt) | Maximum upslope of the arterial pressure waveform from a peripheral artery. It is the maximum rate of the arterial pressure rise during left ventricular contraction |
| Cardiac output (CO) | Volume of blood pumped by the heart measured in liters per minute |
| Cardiac index (CI) | Cardiac output relative to body surface area (BSA) |
| Systolic pressure (SYS) | Systolic blood pressure |
| Diastolic pressure (DIA) | Diastolic blood pressure |
| Mean arterial pressure (MAP) | Averaged systemic blood pressure over one cardiac cycle |
| Pulse rate (PR) | Number of ventricular contractions per minute |
| Stroke volume (SV) | Volume of blood pumped with each heart beat |
| Stroke volume index (SVI) | Stroke volume relative to body surface area (BSA) |
| Systemic vascular resistance (SVR) | The resistance that the left ventricle must overcome to eject stroke volume with each beat |
| Systemic vascular resistance index (SVRI) | SVR relative to body surface area |
| Stroke volume variation (SVV) | The percent difference between SVmin, max and mean |
| Central venous oximetry (ScvO2) | Venous oxygen saturation as measured in the superior vena cava |
| Mixed venous oximetry (SvO2) | Venous oxygen saturation as measured in the pulmonary artery |
| Tissue oxygen saturation (StO2) | A noninvasive continuous assessment of the balance between oxygen delivery and consumption through either cerebral or somatic tissue oximetry |
*A hypotensive event is defined as MAP <65 mmHg for a duration of at least one minute.
How prevalent is intraoperative hypotension (IOH)?
Numerous studies show IOH is strongly associated with risk, especially myocardial injury, acute kidney injury, and mortality.1-8
Acumen HPI software is effective in detecting haemodynamic instability and substantially reducing the amount of intraoperative hypotension when used in surgical patients who require intraoperative haemodynamic monitoring during non-cardiac surgery.15

IOH is common9-11
88% of non-cardiac surgery patients (19,446/22,109) monitored with an arterial line experienced at least one hypotensive event* for at least 1 minute.^11

IOH has elevated risks1,2,11
A wealth of evidence suggests a link between IOH and the increased risk of adverse outcomes – including MI, AKI, and mortality – after non-cardiac surgery.1,2,11

IOH can be reduced
Acumen HPI software has demonstrated a reduction in the duration of IOH by 57%.13
^From a retrospective multicentre observational study that evaluated moderate-to-high risk (ASA status of 3 or 4) non-cardiac surgery patients monitored for hypotension at hospitals that used an invasive arterial line ≥75% of the time.11
*Hypotension/hypotensive event was defined as MAP <65 mmHg for at least one minute.11
Physiology of perfusion
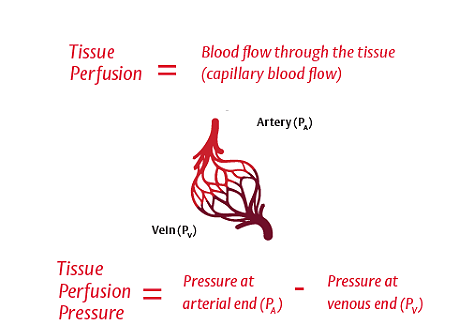
Adequate perfusion requires adequate arterial pressure and cardiac output (CO)
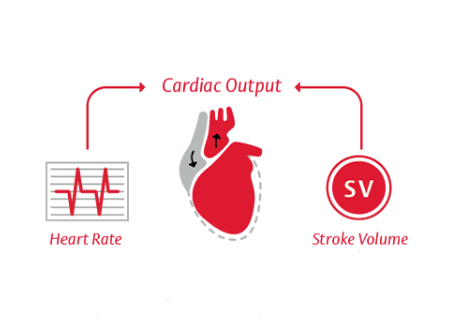
Cardiac Output (CO) = Stroke Volume x Heart Rate
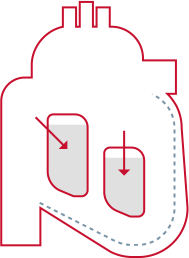
Preload: the tension of myocardial fibers at the end of diastole, as a result of volume in the ventricle
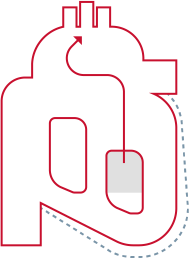
Stroke Volume (SV): volume of blood pumped from the left ventricle per heartbeat
When managing volume, stroke volume variation (SVV) has been proven to be a highly sensitive, reliable, and specific indicator for preload responsiveness in loading conditions induced by mechanical ventilation.9-12
Compatible monitoring platform
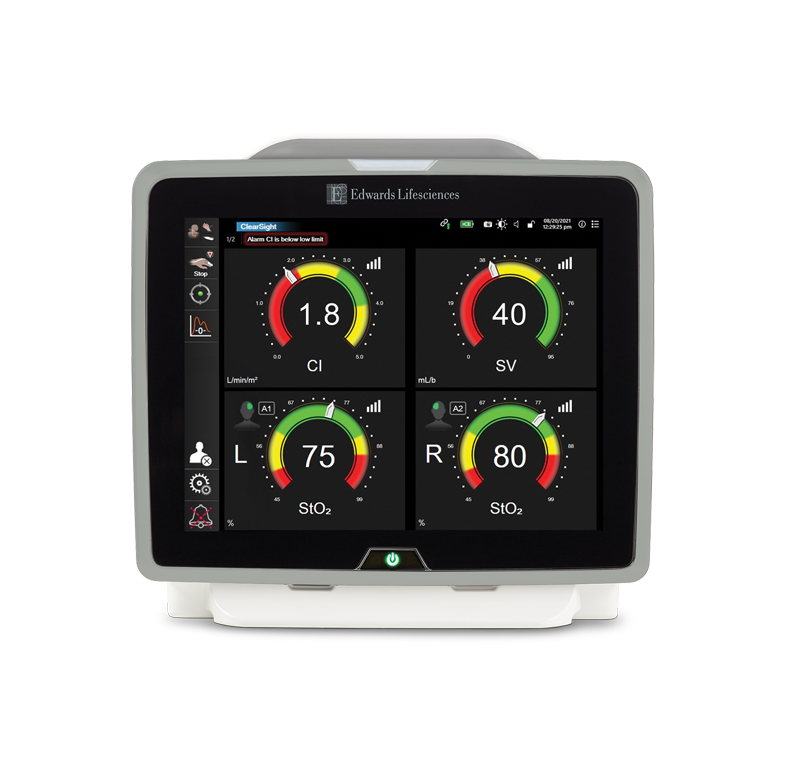
HemoSphere advanced monitoring platform
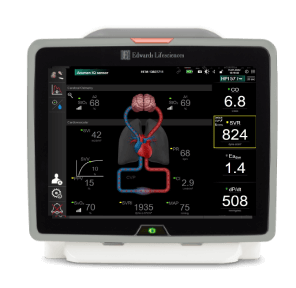
The only modular haemodynamic monitoring platform to offer full-range cuff, sensor and catheter compatibility and first-of-its-kind predictive decision support software, HemoSphere advanced monitoring platform enables proactive, individualised patient management.

Acumen intelligent decision support suite
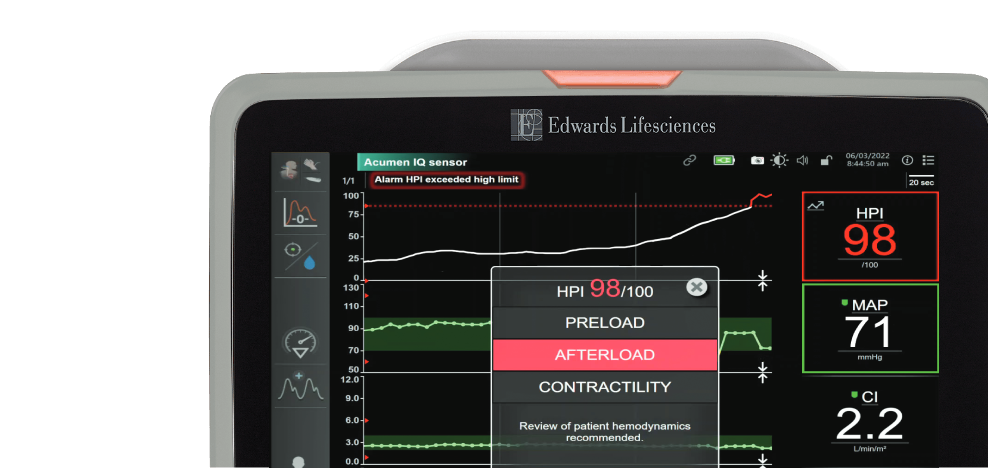
Acumen Hypotension Prediction Index (HPI) software
Acumen Hypotension Prediction Index software is the first predictive technology that provides you with information regarding the likelihood of a patient trending toward a hypotensive event.* 12-14
*A hypotensive event is defined as MAP <65 mmHg for a duration of at least one minute.
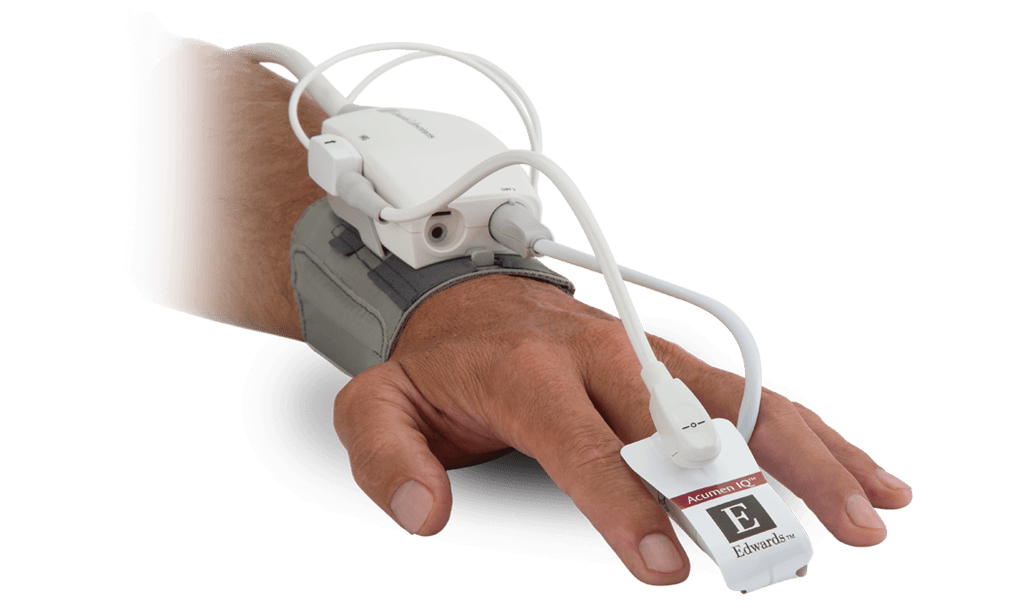
Acumen IQ cuff
The Acumen IQ cuff enables you to unlock the Acumen Hypotension Prediction Index (HPI) software for surgical patients, while delivering continuous blood pressure monitoring and advanced haemodynamic parameters noninvasively.
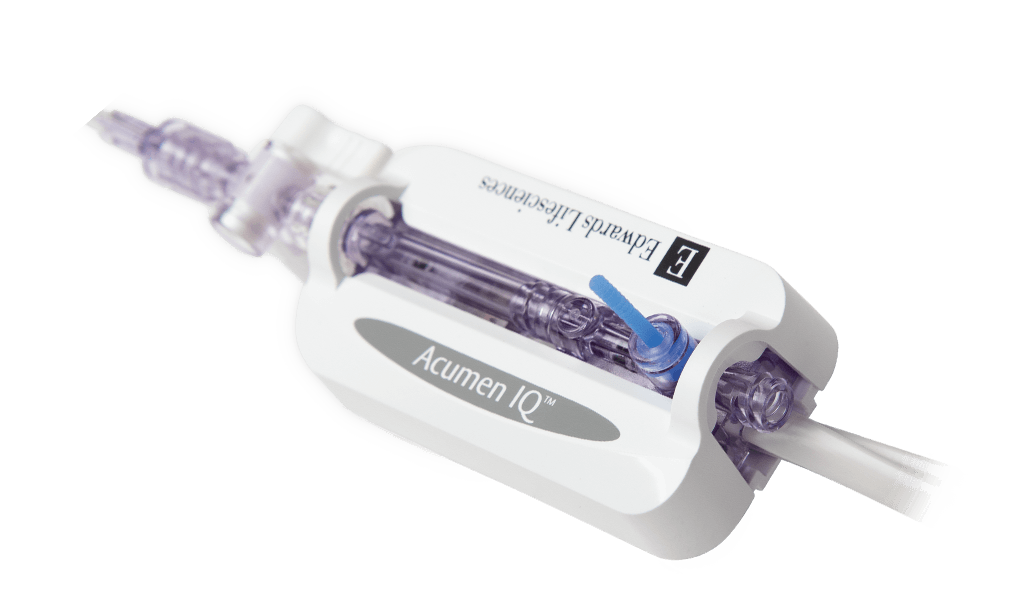
Acumen IQ sensor
The Acumen IQ sensor unlocks Acumen HPI software for surgical and nonsurgical patients. The Acumen IQ sensor automatically updates advanced parameters every 20 seconds, reflecting rapid physiological changes in moderate- to high-risk surgery and patients in the intensive care settings.
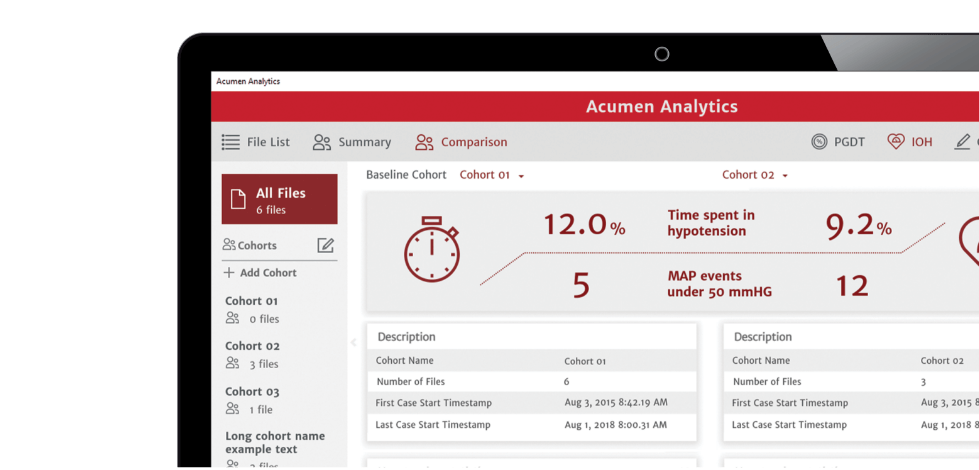
Acumen Analytics software
Acumen Analytics software enables you to retrospectively view and analyse haemodynamic parameters, including mean arterial pressure, providing you insights into the frequency, duration and prevalence of intraoperative hypotension in your practice.
System requirements:
- Minimum 32GB hard drive (minimum) with 3GB available disk space
- Memory: 8GB RAM minimum
- Compatible with Windows 7, 8 and 10 (32 & 64 bit)
- Supports excel files that contain data points in 20-second time intervals
References
- Gregory A, Stapelfeldt WH, Khanna AK, et al. Intraoperative hypotension is associated with adverse clinical outcomes after noncardiac surgery. Anesth Analg. 2021;132(6):1654-1665.
- Wesselink EM, Kappen TH, Torn HM, et al. Intraoperative hypotension and the risk of postoperative adverse outcomes: a systematic review. Br J Anaesth. 2018;121(4):706-721.
- Monk TG, et al. Anesthetic Management and One-Year Mortality After Noncardiac Surgery. Anesth Analg 2005;100:4–10.
- Monk TG, et al. Association between Intraoperative Hypotension and Hypertension and 30- day Postoperative Mortality in Noncardiac Surgery. Anesthesiology 2015; 123:307-19.
- Walsh M, et al. Relationship between Intraoperative Mean Arterial Pressure and Clinical Outcomes after Noncardiac Surgery Toward an Empirical Definition of Hypotension Anesthesiology, 2013;119(3):507-515.
- Sun LY, et al. Association of Intraoperative Hypotension with Acute Kidney Injury after Elective Noncardiac Surgery. Anesthesiology 2015;123:515-23.
- Hirsch J, et al. Impact of intraoperative hypotension and blood pressure fluctuations on early postoperative delirium after noncardiac surgery. British Journal of Anaesthesia, 2015:418–26.
- Bijker JB, et al. Intraoperative Hypotension and Perioperative Ischemic Stroke after General Surgery: A Nested Casecontrol Study. Anesthesiology, 2012;116: 658-664.
- Salmasi, V., Maheshwari, K., Yang, G., Mascha, E.J., Singh, A., Sessler, D.I., & Kurz, A. (2017). Relationship between intraoperative hypotension, defined by either reduction from baseline or absolute thresholds, and acute kidney injury and myocardial injury after noncardiac surgery: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis. Anesthesiology, 126(1), 47-65.
- Bijker JB, van Klei WA, Kappen TH, van Wolfswinkel L, Moons KGM, Kalkman CJ. Incidence of intraoperative hypotension as a function of the chosen definition: literature definitions applied to a retrospective cohort using automated data collection. Anesthesiology 2007; 107: 213e20.
- Shah NJ, Mentz G, Kheterpal S. The incidence of intraoperative hypotension in moderate to high risk patients undergoing noncardiac surgery: A retrospective multicenter observational analysis. J Clin Anesth. 2020;66:109961.
- Ward H. van der Ven, Denise P. Veelo, Marije Wijnberge, Björn J.P. van der Ster, Alexander P.J. Vlaar, Bart F. Geerts, One of the first validations of an artificial intelligence algorithm for clinical use: The impact on intraoperative hypotension prediction and clinical decisionmaking, Surgery, Volume 169, Issue 6, 2021, Pages 1300-1303, ISSN 0039- 6060, https://doi.org/10.1016/ j.surg.2020.09.041.
- Prospective, single-arm, multicenter study in noncardiac surgical patients requiring arterial line monitoring compared to a historical control. Data on file.
Medical device for professional use
For a listing of indications, contraindications, precautions, warnings, and potential adverse events, please refer to the Instructions for Use (consult eifu.edwards.com where applicable).
Acumen Analytics software is a tool for data analysis, not a medical device.