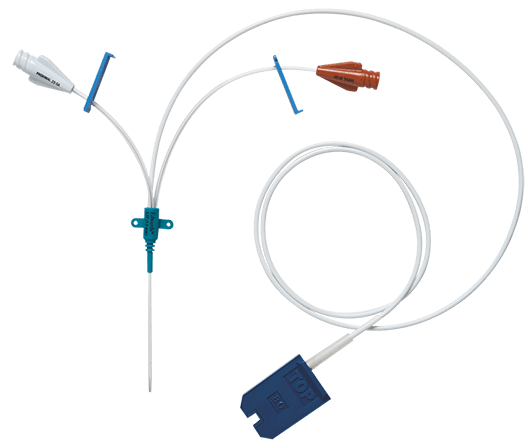
PediaSat oximetry catheter
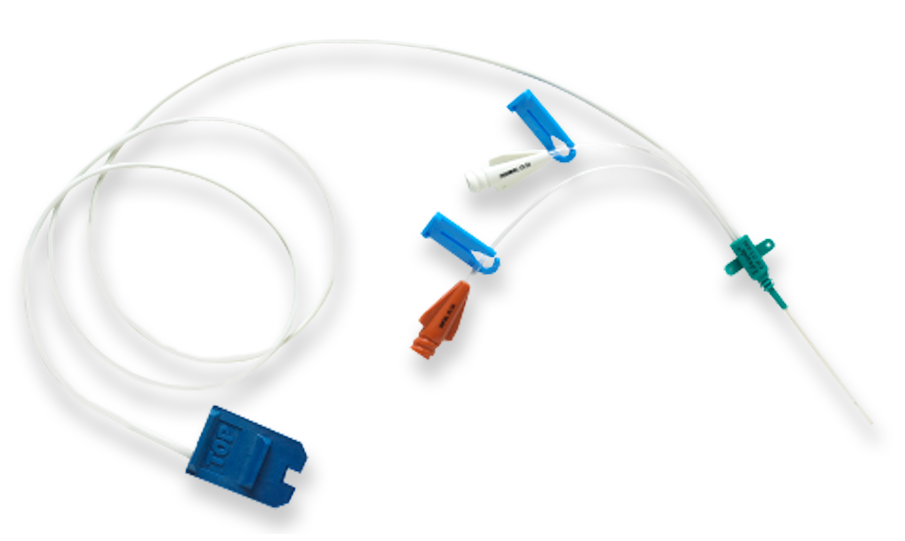

PediaSat oximetry catheter is the first and only pediatric oximetry catheter with continuous ScvO2 monitoring for proactive management of tissue hypoxia.1-2 Continuous, real-time monitoring of central venous oxygen saturation (ScvO2) offers early recognition of critical changes in oxygen delivery that may not be identified by less sensitive indicators, such as traditional vital signs or intermittent sampling.3
PediaSat oximetry catheter
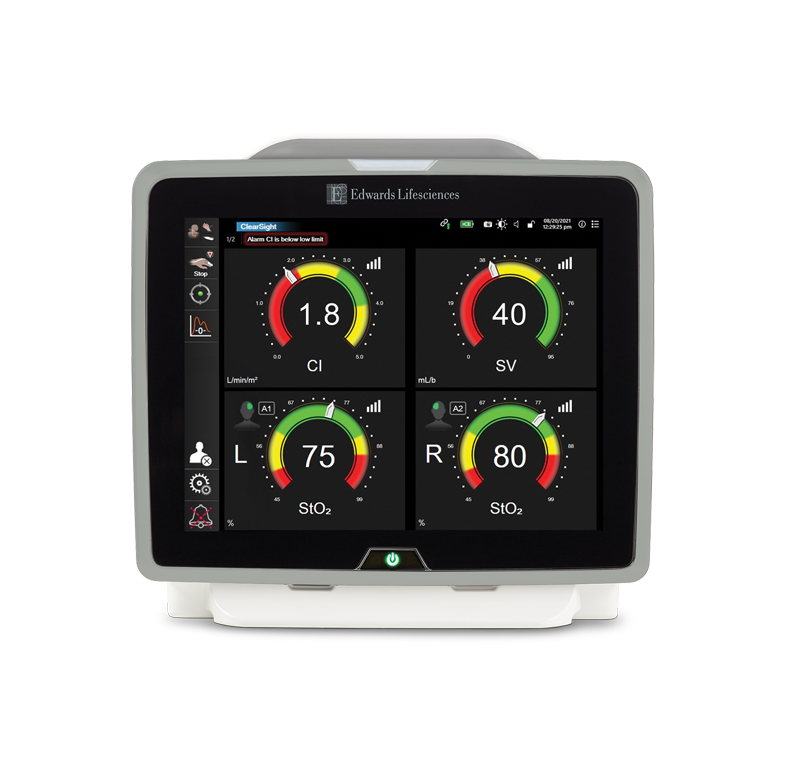
Continuous ScvO2 monitoring
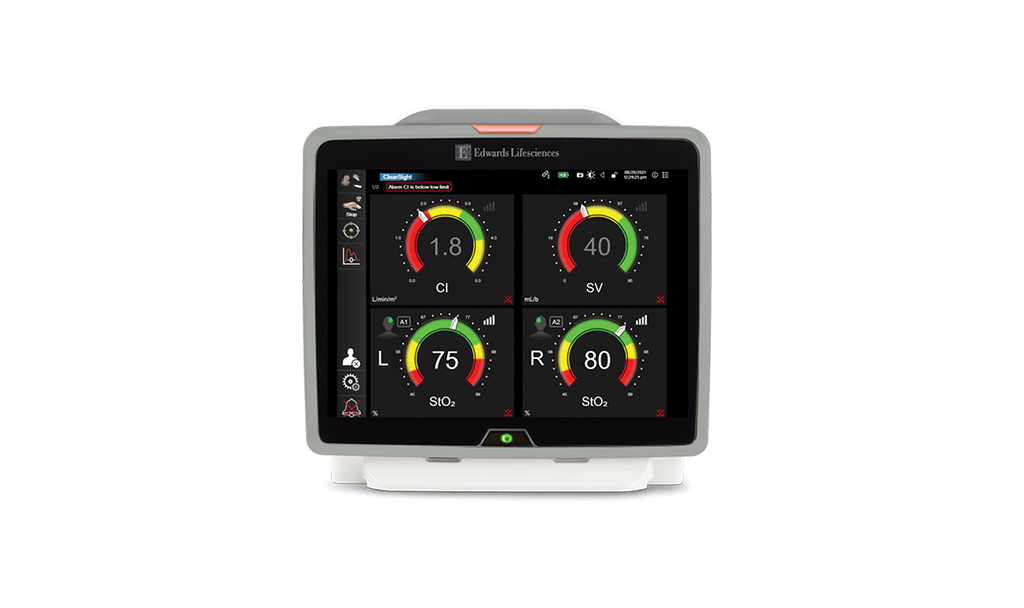
Early warning of oxygen imbalance allows early intervention.
Early indication with continuous ScvO2 monitoring offers you the ability to detect and prevent tissue hypoxia − early− in your complex pediatric patients.4
Continuous ScvO2 monitoring reveals the root cause of oxygen imbalance, enabling you to proactively determine appropriate therapy. Real-time insight into the adequacy of cardiac output allows immediate assessment of your patient's clinical response to therapy − to help you stay ahead of tissue hypoxia and stages of sepsis.4
Continuous ScvO2 monitoring helps guide therapy and enables early intervention:
You can use haemodynamics to manage pediatric and neonatal septic shock patients in accordance with ACCM-PALS Clinical Practice Parameters5
PediaSat oximetry catheter model numbers
| Lumens | Length (CM) | Size F (MM) | |
| XT248SP | 2 | 8 | 4.5 |
| XT3515SP | 3 | 15 | 5.5 |
Philips IntelliVue SO2 module
| Model number | Description |
| M1011A* | SO2 Module |
| M1011A #A01* | Optical Module |
*Philips Healthcare model numbers
PediaSat catheter - accessories
| Description | Length (cm) | |
| OM2E | Edwards oximetry optical module | 335 |
| HEMOXSC100 | HemoSphere oximetry cable | 292 |
Clinical application
See clearly. Stay ahead.
PediaSat oximetry catheter offers an early warning for compromised or inadequate oxygen delivery
Continuous measurement of ScvO2 in combination with other surrogates of organ perfusion (vital signs, lactate, etc.) can be used as a reliable monitor of cardiocirculatory function.6
- Detect acute changes in systemic oxygen delivery and consumption7
- Identify decreases in systemic oxygen delivery that otherwise would not be identified using intermittent sampling8
- Evaluate oxygen reserve to decide routine interventions (including suctioning, turning, etc.) to minimize patient compromise and maximize outcome.9
Can optimize hemodynamic management in complex pediatric patients.1,2,5,9,10
- Congenital heart disease and other complex cardiac patients1,2
- Sepsis and septic shock5
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)9
- Other high-risk patients10
Convenient, accurate and easy to use.11
PediaSat oximetry catheter provides:
- Simplicity and flexibility − uses the same insertion techniques as central lines in typical pediatric insertion sites, including subclavian and internal jugular
- Continuous ScvO2 monitoring, pressure monitoring and infusion of solutions
- Accurate oxygenation status1
- Double and triple lumens to monitor and administer solutions
Edwards clinical education
Hemodynamic education empowering clinical advancement
With a long-term commitment to improving the quality of care for surgical and critical care patients through education, Edwards clinical education meets you no matter where you are in the learning process — with a continuum of resources and tools that continuously support you as you solve the clinical challenges facing you today, and in the future.
Product implementation
Product setup
References
- Ranucci, M., et al. Continuous monitoring of Central venous oxygen saturation (PediaSat) in pediatric patients undergoing cardiac surgery: a validation study of a new technology. Journal of cardiothoracic and vascular anesthesia, Vol. 22, No. 6, December 2008, p. 847-852.
- Mohseni, H, et al. Evaluation of a new pediatric continuous oximetry catheter. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2011;12(4): 437-441.
- Liakopoulos et al “An Experimental and Clinical Evaluation of a Novel Central Venous Catheter with Integrated Oximetry for Pediatric Patients Undergoing Cardiac Surgery” Anesthesia & Analgesia: December 2007 - Volume 105 - Issue 6 - p 1598-1604[55].
- Reinhart K, et al. Continuous central venous and pulmonary artery oxygen saturation monitoring in the critically ill. Intensive Care Med. 2004;30(8):1572-8.
- de Oliveira, CF, et al. An outcomes comparison of ACCM/PALS guidelines for pediatric septic shock with and without central venous oxygen saturation monitoring. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2007, Vol. 8,No. 3 (Suppl.).
- Mahajan A, et al. An experimental and clinical evaluation of a novel central venous catheter with integrated oximetry for pediatric patients undergoing cardiac surgery. Pediatric Central Venous Oximetry. Anest Anal. 2007;Vol.105, No. 6, 1598.
- Tweddell JS, et al. Postoperative management in patients with complex congenital heart disease. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg Pediatr Card Surg Annu. 2002;5:187-205.
- Tweddell JS, et al. Patients at risk for low systemic oxygen delivery after the Norwood procedure. Ann Thorac Surg. 2000;69(6):1893-9.
- Sanders CL. Making clinical decisions using SvO2 in PICU patients. Dimens Crit Care Nurs. 1997;16(5):257-64.
- Ranucci et al. Central venous oxygen saturation and blood lactate levels during cardiopulmonary bypass are associated with outcome after pediatric cardiac surgery. Critical Care 2010.
- Ranucci, M, et al. Near-infrared spectroscopy correlates with continuous superior vena cava oxygen saturation in pediatric cardiac surgery patients. Pediatric Anesthesia 2008. 18:1163-1169.
- Rivers EP, Katranji M, Jaehne KA, Brown S, Abou Dagher G, Cannon C, Coba V. Early interventions in severe sepsis and septic shock: a review of the evidence one decade later. Minerva Anestesiol. 2012 Jun;78(6):712-24. Epub 2012 Mar 23. PMID: 22447123.
Medical device for professional use
For a listing of indications, contraindications, precautions, warnings, and potential adverse events, please refer to the Instructions for Use (consult eifu.edwards.com where applicable).